Emerging space nations: supporting sustainable development and economic growth
The benefits of space technologies and applications towards supporting society.
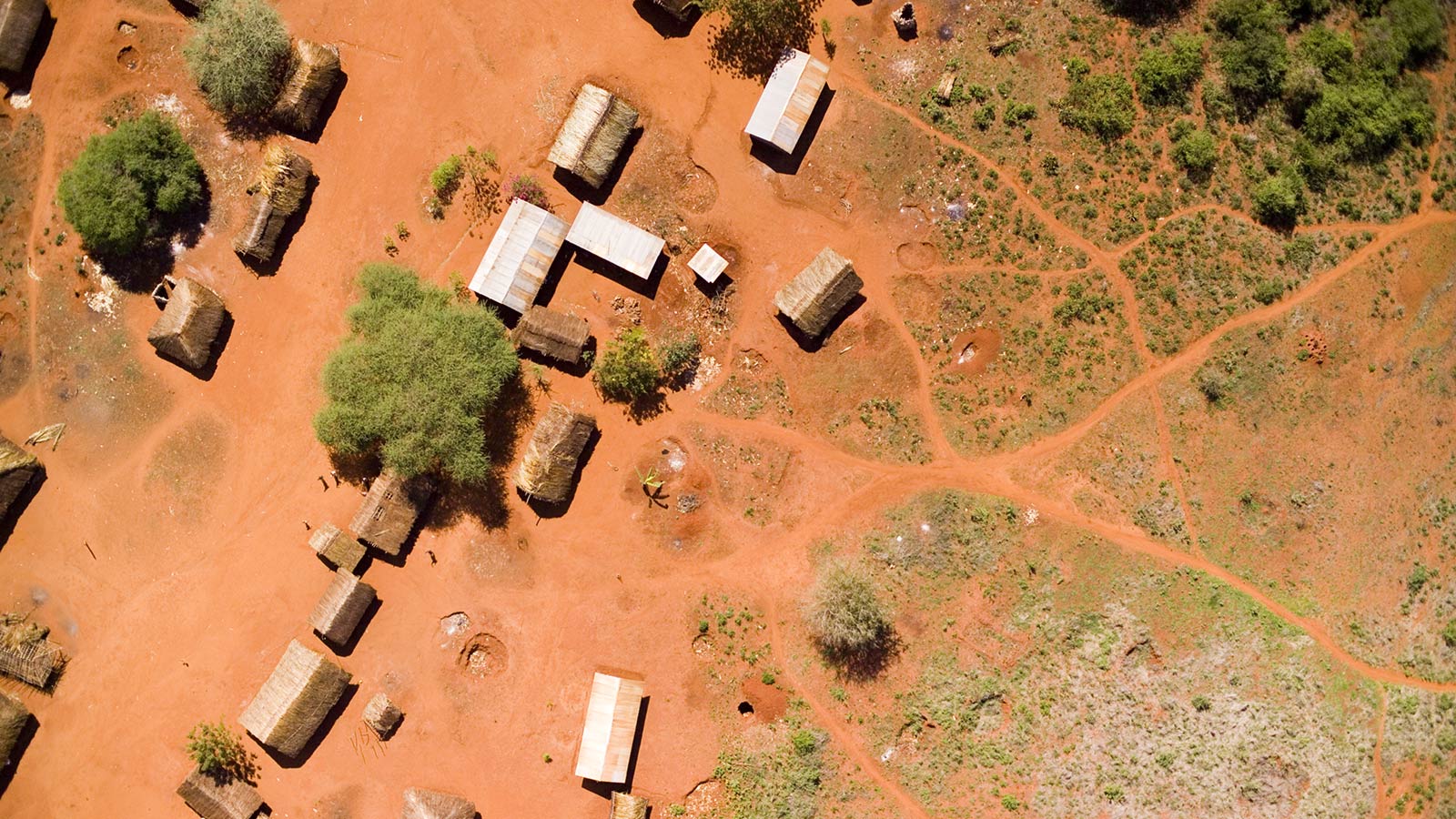
The benefits of space technologies and applications towards supporting society have become increasingly important in the global agendas of sustainability and development. This has prompted the establishment of the “Space2030” agenda, which seeks to outline a comprehensive and inclusive long-term vision for space, detailing how space-based data, space infrastructure, services and applications can address goals in the major frameworks, above all towards the achievement of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. The four pillars of Space2030 cover space economy, focusing on the development of space-derived economic benefits; space society, to advance the societal benefits of space-related activities; space accessibility, allowing access to space for all; and space diplomacy, which strives to build partnerships and strengthen international cooperation and the governance of space activities. Within its initiatives, Space2030 aims to encourage the advancement of emerging space nations.
Indeed, all four of its main strategic objectives mentioned above can be addressed in some way by the development of the space sector for these new players, from encouraging industry, innovation and infrastructure, and economic growth within the country, to supporting solutions for climate action, water management and sustainable land management. It also inspires new collaborations and cooperation with established space actors and the broader space community. Hence, it is important to identify these emerging space nations, their visions for future space activities, and how this can target the Space2030 agenda. This paper aims therefore to categorize the countries that have indicated new investments and development within the space sector, and to ascertain the most promising activities within the different geographic regions, including MENA, Africa, South America, North America, Europe, Australia and Asia. Countries such as the United Arab Emirates, Singapore, and Morocco have begun, for example, to increase space activities or have shown interest in establishing strategic goals. It explores the challenges and potential drivers that will affect their progress in instituting or developing a space sector, as well as the geopolitical implications on their advancement and the types of partnerships that have already been established.
Finally, the paper touches upon the vision for their evolution, and how the creation of a space sector can address sustainable development and economic growth.

Contact us